We deliver to you every day from 7:00 to 23:00
Understanding Valve End Connections – Flanged, Threaded, Socket Weld and Butt Weld
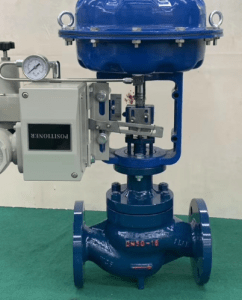
In this Blog We’re going to explore Valve End Connections – Flanged, Threaded, Socket Weld and Butt Weld, and why choosing the right connection type makes a major difference in the performance of any industrial pipeline. End connections do much more than join a valve to a pipe – they influence how the medium flows, how easily the valve can be installed or serviced, and how well it maintains consistent performance over time.
As a Valve Manufacturer in Europe, we produce valves with precisely machined end connections that deliver stable flow and dependable performance across oil, gas, power, and process industries.
How Valve End Connections Work
Valve end connections form the interface between a valve and the pipeline. They determine how the valve fits into the system, how the fluid or gas travels through it, and how secure the joint remains during operation. Choosing the right connection type and valve orientation helps prevent backflow issues and controls pressure drop within the pipeline.
- Flanged Connections: Joined with bolts and gaskets, these connections allow easy assembly, disassembly, and inspection during plant maintenance.
- Threaded Connections: Common in smaller pipelines, they use screw-type threads for a tight fit and quick installation.
- Socket Weld Connections: The pipe end is inserted into a socket and welded around the joint – suitable for high-pressure or high-vibration systems.
- Butt Weld Connections: Pipes are directly welded to the valve ends, providing a smooth bore and continuous flow path with minimal turbulence.
Each connection offers a unique blend of strength, installation convenience, and flow characteristics suited to different process requirements.
Types of Valve End Connections
The selection of Valve End Connections – Flanged, Threaded, Socket Weld and Butt Weld depends on several variables, including the pipeline’s size, the working medium, and the system’s operating conditions.
- Flanged End Connections – Best for large pipelines and systems that require periodic disassembly or valve replacement.
- Threaded End Connections – Practical for smaller lines where welding isn’t feasible or required.
- Socket Weld End Connections – Used in compact systems handling higher pressures, providing secure, permanent joints.
- Butt Weld End Connections – Ideal for continuous process lines where flow smoothness and joint strength are priorities.
Materials & Pressure Classes
Valves Only offers valves in stainless steel, carbon steel, and various alloy grades. Each material is selected for its ability to resist wear, temperature fluctuation, and chemical exposure.
Pressure ratings range from PN10 to PN400 or ANSI 150 to ANSI 2500, allowing our valves to perform reliably in both moderate and demanding operating conditions. Selecting the proper combination of material and pressure class supports consistent operation and reduces the risk of joint failure.
Design and Flow Mechanism
The design of valve end connections determines how efficiently a medium moves through the valve body. A smooth flow path limits pressure drop, while robust joints reduce the chance of leakage or flow reversal.
Our engineering focuses on accurate alignment, tight sealing surfaces, and refined bore geometry. Every valve is built to maintain stable operation under load variations and cyclic pressure.
- Flow Direction: Clear markings on each valve body support correct valve orientation during installation.
- Pressure Drop: Socket and butt weld designs provide minimal internal resistance for steady flow.
- Leak Control: Flanged joints use precision gaskets, while welded ends rely on metal-to-metal strength to prevent seepage.
Each connection design undergoes testing under standards like API 598, ASME B16.34, and ISO 5208 to verify pressure retention and structural consistency before delivery.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Valve End Connections
Selecting the most suitable connection type involves assessing several technical and operational factors:
Evaluating these parameters before selection helps avoid performance issues, frequent repairs, and connection-related downtime.
- Type of Fluid or Gas: Aggressive media such as acids or hydrocarbons require welded or corrosion-resistant materials.
- Operating Conditions: High-pressure or high-temperature lines typically demand socket or butt weld joints for additional joint strength.
- Maintenance Requirements: Flanged ends are convenient when periodic removal or inspection is part of the maintenance cycle.
- System Layout: Threaded valves fit well in compact or portable systems, whereas welded joints are used in fixed, high-load environments.
- Energy Loss and Flow Uniformity: For continuous operations, butt weld connections help maintain consistent velocity and lower turbulence.
- Future Modifications: Flanged ends make future valve replacement or system expansion simpler and faster.
Why Valve End Connections Are Vital
The end connection is often a hidden but crucial aspect of valve performance. Even a well-designed valve can fail to perform if the connection is mismatched with the application. Incorrect selection or installation can cause leaks, vibration, flow disturbances, or even line rupture under stress.
By contrast, well-chosen Valve End Connections – Flanged, Threaded, Socket Weld and Butt Weld contribute to smoother operation, better control over the process medium, and fewer interruptions during production.
Why Choose Valves Only Europe
We build our valves with precision, consistency, and long-term system stability in mind. Our Valve End Connections – Flanged, Threaded, Socket Weld and Butt Weld are crafted to support accurate flow control, reduce unnecessary energy loss, and maintain performance even in demanding process conditions.
Whether you’re handling gas, steam, water, or industrial fluids, Valves Only Europe can help you determine which end connection suits your pipeline setup. Share your process medium, temperature, and line pressure – our engineering team will recommend the most suitable configuration for your system’s operation.
Recent Posts
- Pressure Seal Gate Valves: Design Principle and High-Pressure Service
- Valves Used in Chemical Processing Plants
- Single Offset vs Double Offset vs Triple Offset Butterfly Valves – What’s the Difference?
- Globe Valve vs Ball Valve for Flow Control Applications: A Complete Comparison
- Forged vs Cast Valves: Differences, Strength & Applications for Corrosive Environments